CD66b Antibodies
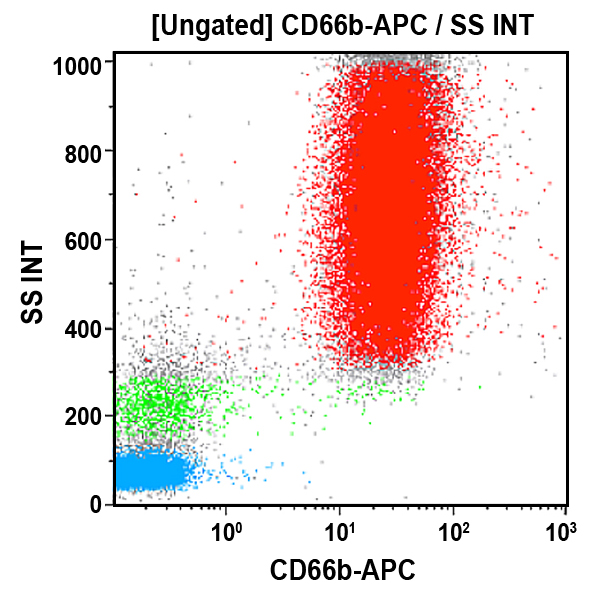
The CD66 antigens were originally described as granulocyte-specific activation antigens, related to the carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA) previously described on colon cancer cells. The CEA/CD66 gene group belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) gene superfamily. Among the CD66 cluster, CD66b (also known as CGM6) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored glycoprotein of 95-100 kDa. CD66b is thought to play a role in the regulation of the adhesive activity of CD11/CD18 via signal transduction in neutrophils. It is strongly expressed by myelocytes, metamyelocytes, neutrophils and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. CD66b is weakly expressed by promyelocytes.
| Clone: 80H3 | Isotype: IgG1 Mouse |
| The 80H3 antibody does not react with peripheral lymphocytes and monocytes. | |